FileSchematic diagram of the human eye en.svg Wikipedia, the free
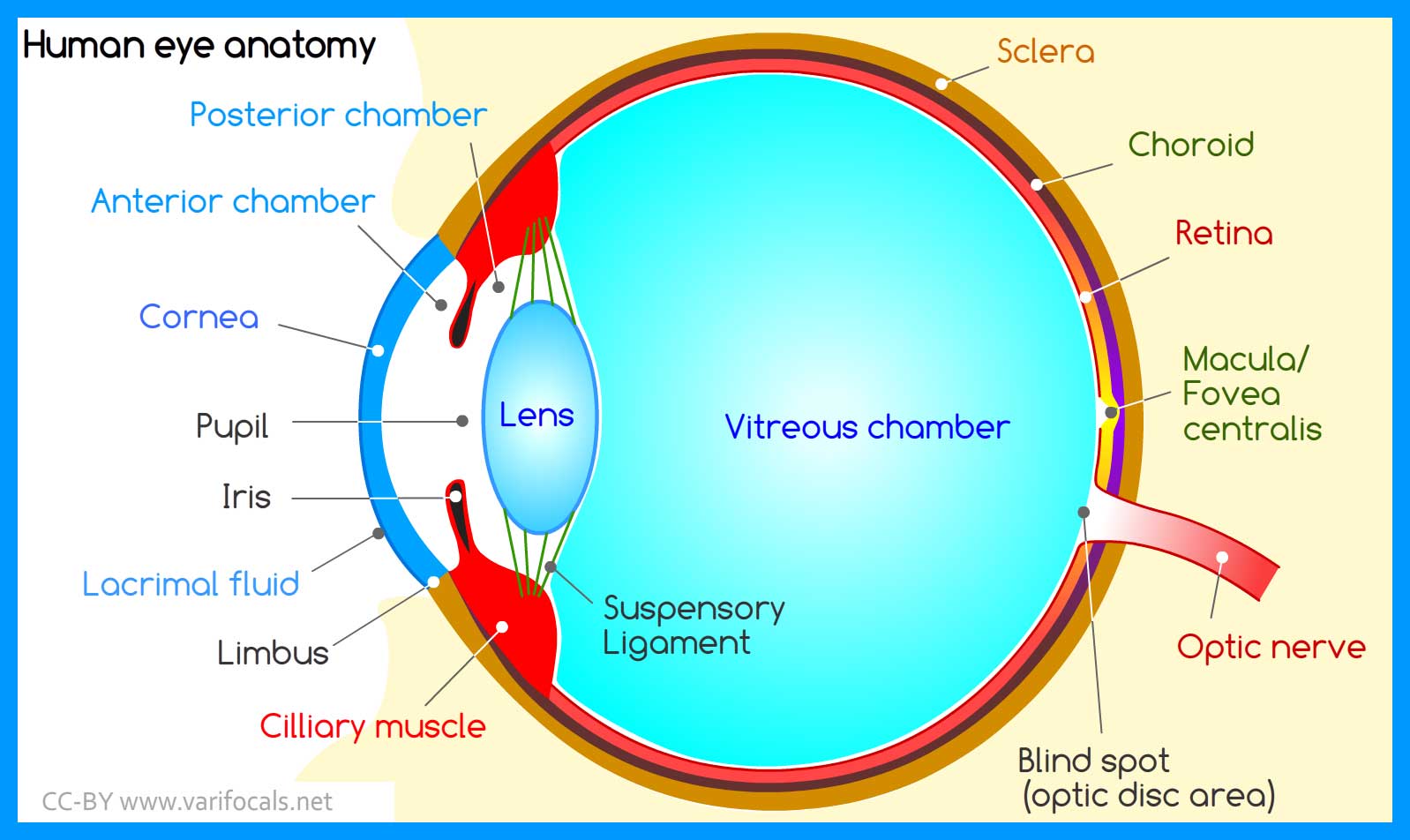
Human Eye Anatomy, Structure and Function
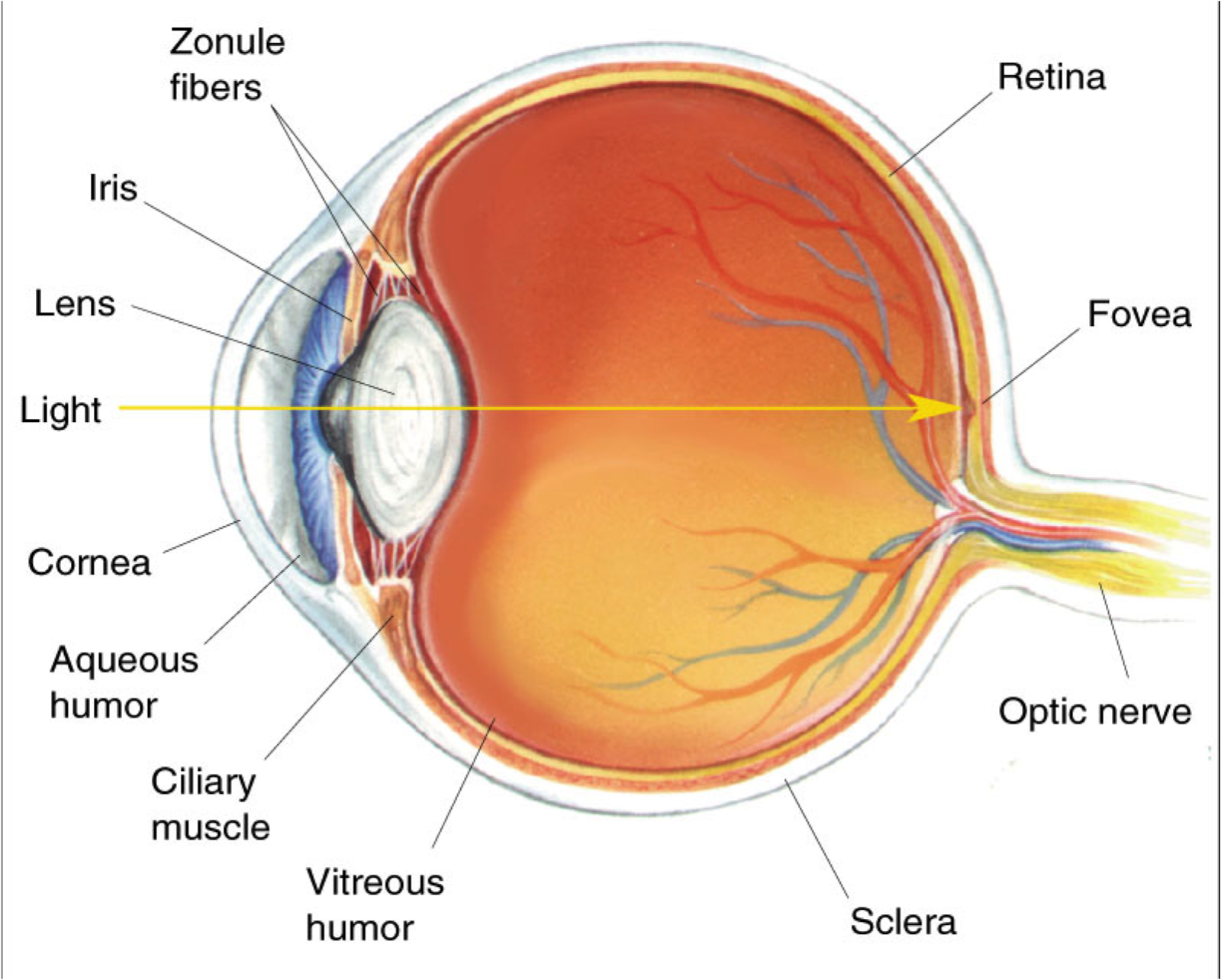
The human eye is the sensory organ responsible for vision (sight perception). It consists of two fluid-filled cavities separated by a lens (anterior = aqueous humour, posterior = vitreous humour); The lens is attached to ciliary muscles, which can contract or relax to change the focus of the lens; The amount of light that enters the eye via the pupil is controlled by the constriction and.

FileSchematic diagram of the human eye en.svg Wikipedia, the free
The light passing through cornea, pupil, and lens gets focused on the retinal membrane. In addition to tissue components, retina is made up of two types of cells: rod cells and cone cells. The.

Brain Post How Big is Your Blind Spot? Human eye
The diagram below points to different parts of the human eye. The human eye. Choose the correct labels for the parts shown. Choose all answers that apply: A is the crystalline lens. A A is the crystalline lens. B is the aqueous humour. B B is the aqueous humour. C is the iris. C C is the iris. D is the cornea. D D is the cornea.
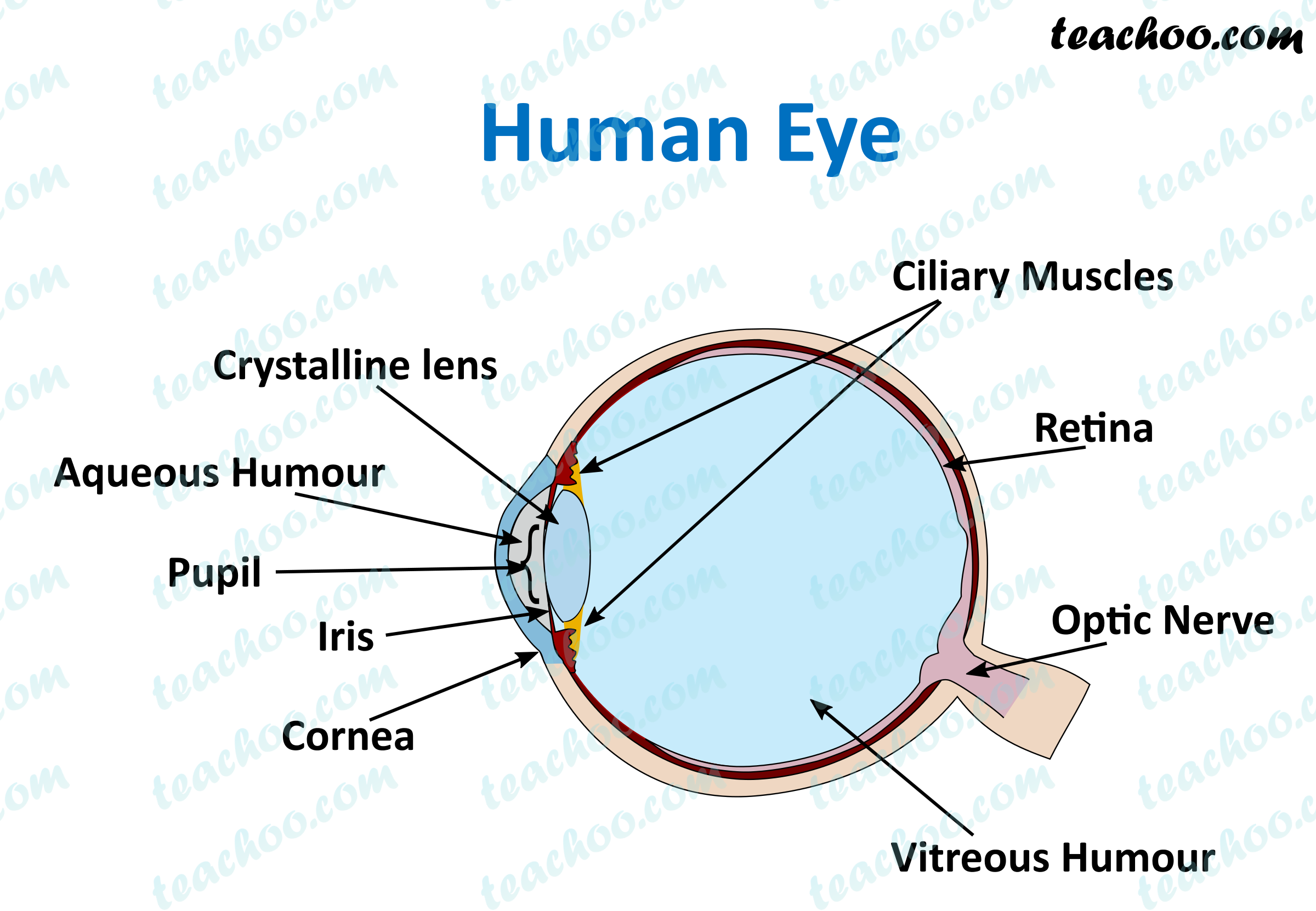
Human Eye Different Parts and their functions Class 10 Teachoo
Biology Article Diagram Of Eye Diagram Of Eye The human eye is responsible for the most important function of the human body, the sense of sight. It consists of several distinct parts that work in coordination with each other. The most common eye diseases include myopia, hypermetropia, glaucoma and cataract.
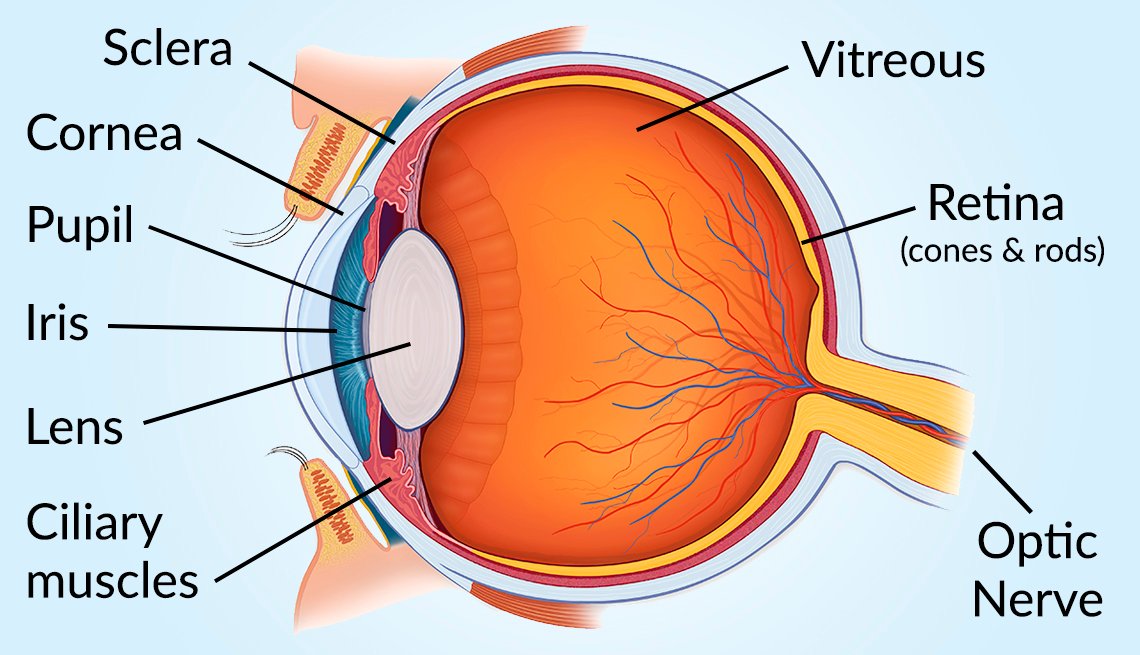
Vision and Eye Diagram How We See
The human eye is a part of the sensory nervous system. Labeled Diagram of Human Eye . The eyes of all mammals consist of a non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion within the retina which receives light, adjusts the dimensions of the pupil, regulates the availability of melatonin hormones, and also entertains the body clock.

Diagram human eye anatomy with label Royalty Free Vector
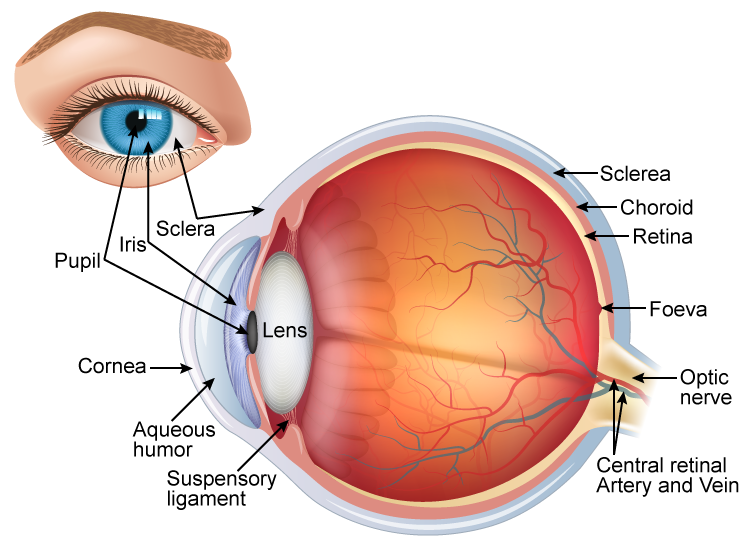
Cornea Lens Retina Optic nerve Pupil Schlera Vitrous humour Iris Download Exercise Tweet Rights: The University of Waikato Te Whare Wānanga o Waikato Published 23 February 2021 Referencing Hub media The human eye has several structures that enable entering light energy to be converted to electrochemical energy.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure and Function of the Human Eye
Macula. The central portion of the retina that allows us to see fine details. Optic nerve. A bundle of nerve fibers that connect the retina with the brain. The optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colors to a part of the brain called the visual cortex, which assembles the signals into images and produces vision. Posterior chamber.
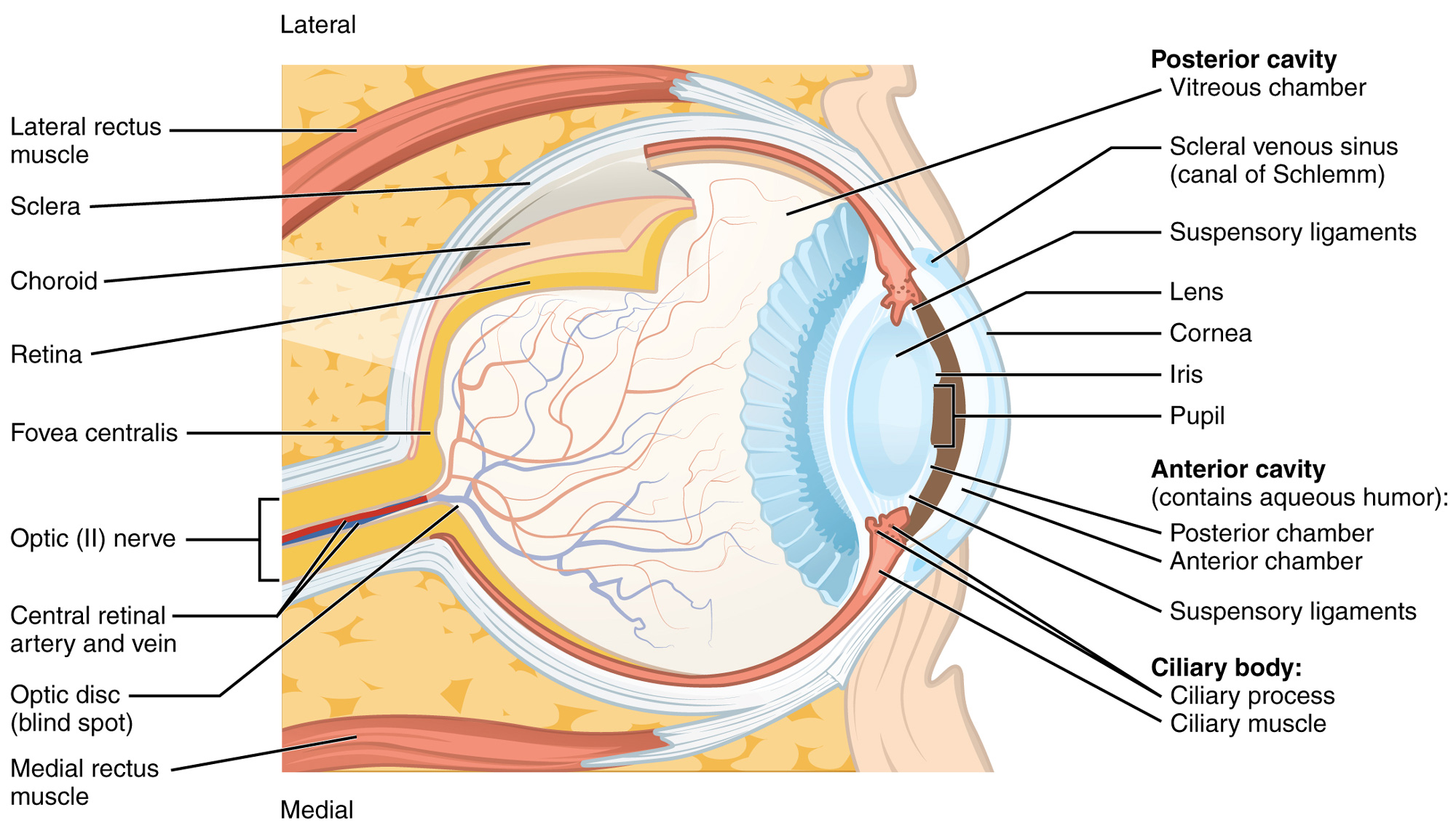
A Detailed Look at the Eye The Canadian Association of Optometrists
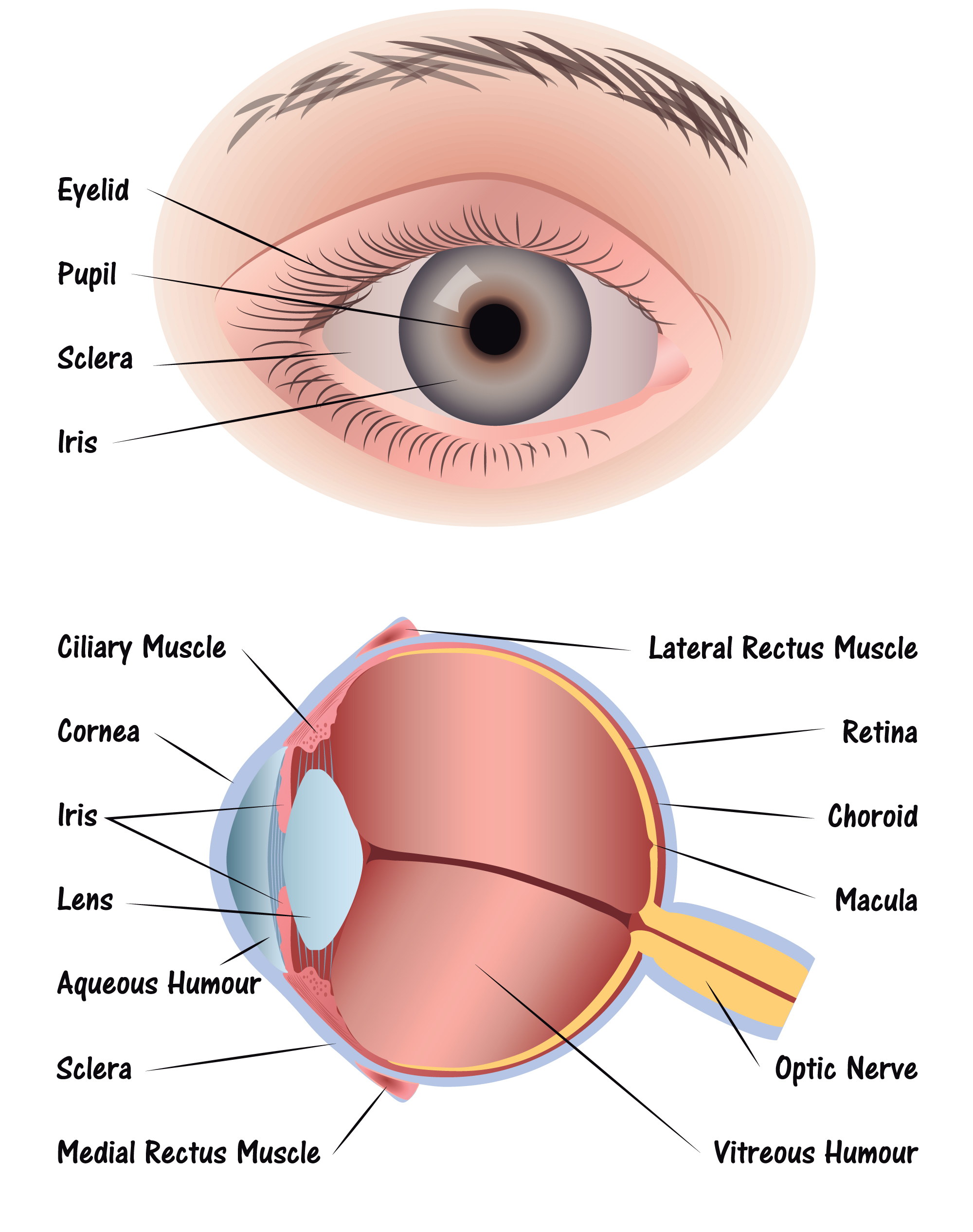
6 min read Your eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part (what you see in the mirror) includes: Iris: the colored part Cornea: a clear dome over the iris.

Human Eye Anatomy Parts of the Eye and Structure of the Human Eye
A human eye is roughly 2.3 cm in diameter and is almost a spherical ball filled with some fluid. It consists of the following parts: Sclera: It is the outer covering, a protective tough white layer called the sclera (white part of the eye). Cornea: The front transparent part of the sclera is called the cornea.

Human Eye Anatomy Parts of the Eye and Structure of the Human Eye
Cornea: The clear, dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye. Fovea: A tiny pit located in the macula of the retina that provides the clearest vision of all. Iris: The colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye by changing the size of the pupil. Lens: A crystalline structure located just behind the iris.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/eye-conjunctiva-871453538-5a26c6ad22fa3a0037d5edad.jpg)
How the Human Eye Works (Structure and Function)
How Do the Eyes Work? Eye Anatomy (16 Parts of the Eye & What They Do) Summary How Do the Eyes Work? Light is reflected when you focus on an object and enters the eye through the cornea. As the light passes through, the dome-shaped nature of the cornea bends light, enabling the eye to focus on fine details.
draw a neat and labelled diagram of structure of the human eye slwbyx77
Diagram of human eye anatomy with label illustration. Download a free preview or high-quality Adobe Illustrator (ai), EPS, PDF, SVG vectors and high-res JPEG and PNG images.
Eye Diagram Cliparts.co
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve. Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor. The iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. Light is focused by the lens and goes.
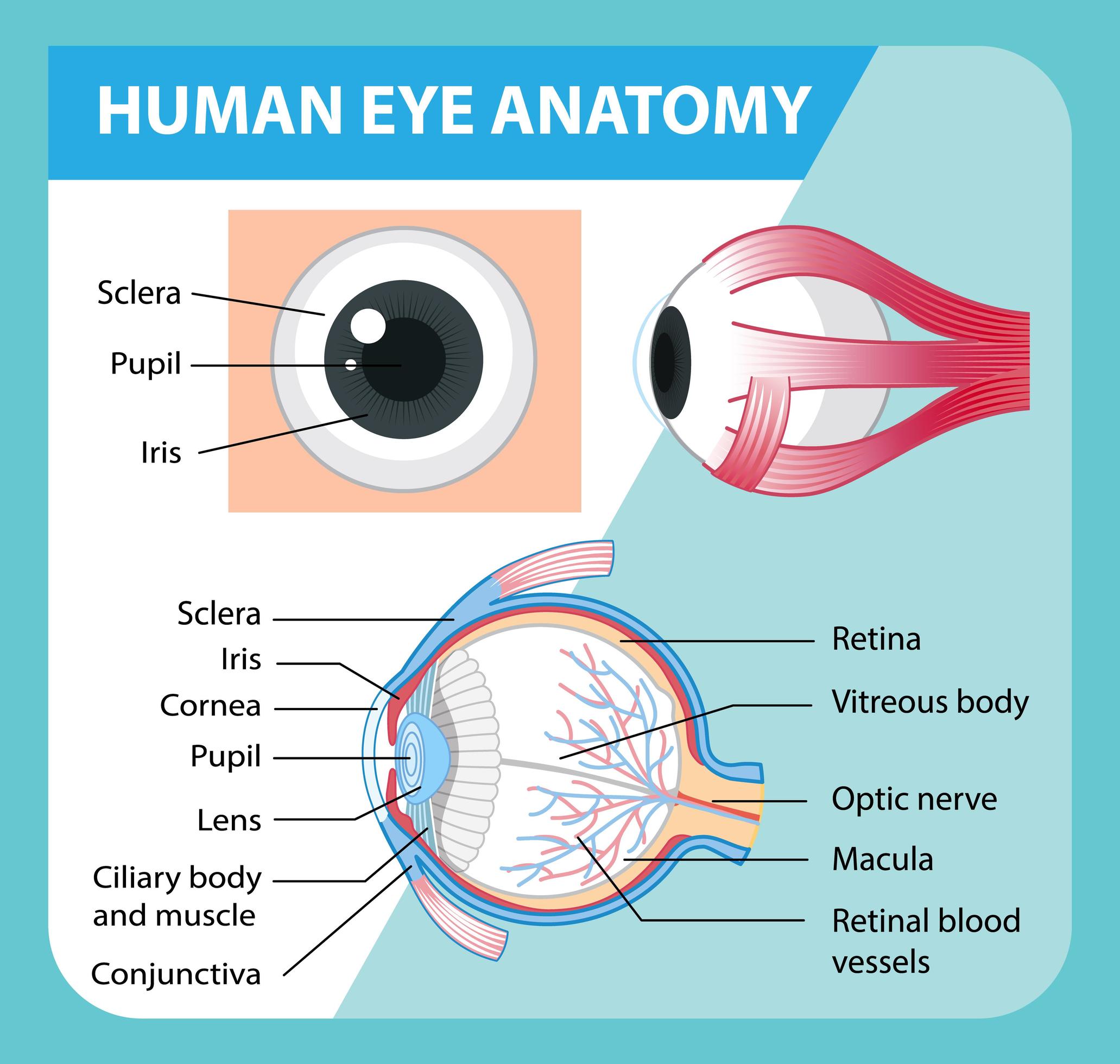
Diagram of human eye anatomy with label 1848847 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The eye is protected from mechanical injury by being enclosed in a socket, or orbit, which is made up of portions of several of the bones of the skull to form a four-sided pyramid, the apex of which points back into the head.

Diagram showing the different parts of the eye Parts of the eye, Eye
Here are descriptions of some of the main parts of the eye: Cornea: The cornea is the clear outer part of the eye's focusing system located at the front of the eye. Iris: The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
OUR EYES WORK LIKE CAMERA’S! Discovery Eye Foundation
Take a look at the diagram of the eyeball above. Here you can see all of the main structures in this area. Spend some time reviewing the name and location of each one, then try to label the eye yourself - without peeking! - using the eye diagram (blank) below. Unlabeled diagram of the eye. Click below to download our free unlabeled diagram of.